Lung Infections - Pnuemonia, h1n1, Influenza ( flu)
Lung infections are one of the most common medical conditions , especially among elderly people across the world. .
How Lung Infection Occurs
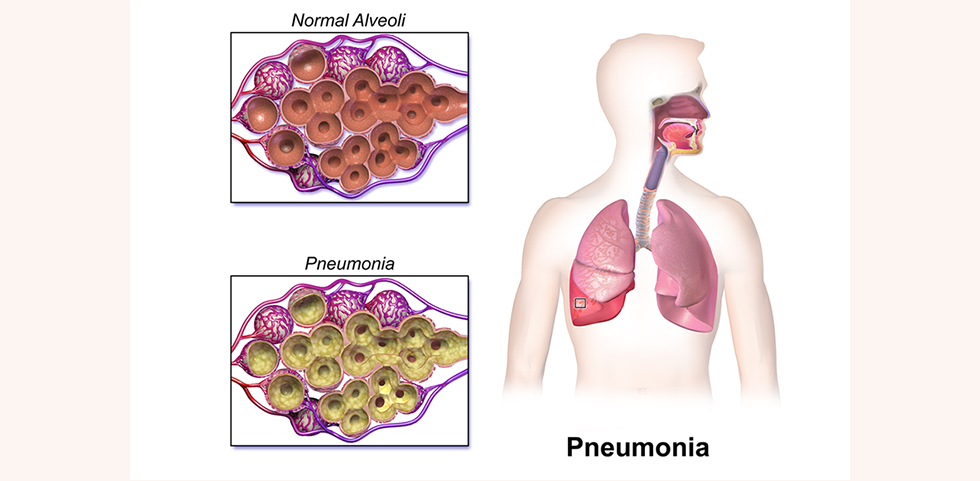
Pneumonia happens when bacteria, viruses, and less commonly fungi collect in a person's air sacs and begin to grow. The air sacs may become filled with pus and fluid, which can make breathing more difficult, cause chest pain, and lead to a cough that is different from a person's usual chronic cough associated with their disease. Bacterial and some of viral pneumonia may be prevented through proper vaccinations.
Symptoms of a Lung Infection
- Fever
- Increased Shortness of Breath
- Productive Cough
- Changes in Mucus
- Pleuritic Chest Pain
- Asthma
Brain infections - Meningitis, Encephalitis, Brain Abscess
These are relatively less common but very serious infections. Patient mostly requires hospitalization in ICU.
Infections can cause inflammation of the brain (encephalitis). Viruses are the most common causes of encephalitis.
Infections can also cause inflammation of the layers of tissue (meninges) that cover the brain and spinal cord—called meningitis. This is mostly commonly by bacteria and Tuberculosis Very often both brain parts may be involved called meningoencephalitis. These cases require MRI, obtaining of CSF through lumbar puncture and badic advanced testing on fluid for ascertaining exact infection.
It is of utmost importance to follow a proper sequence of treatment and choice of antibiotics, antivirals has to be correct from day1 while test reports are awaited. The infectious diseases specialist is best person to choose an initial antibiotic, antiviral medicines so this goal can be achieved.
Abdominal Infections - Hepatitis, Peritonitis, Liver Abscess.
Intra-abdominal infection is a broad term that encompasses a number of infectious processes, including peritonitis, cholangitis, abdominal abscesses e.g. amoebic liver abscess, pyogenic liver abscess.
These infections range from mild to fatal illnesses. Patients present with fever, abdominal pain, general condition of patient like pulse rate and blood pressure may be severely affected in case of serious infections. Owing to huge amount of bacteria load and other microorganisms like fungus- candida , treatment may be difficult Often in serious cases surgery is needed.
Heart Infections- Infective Endocarditis
Here are three primary types of heart infection:
Endocarditis is an infection of the endocardium, which is the inner lining of your heart chambers and heart valves. Most people who develop endocarditis have damaged heart valves or other heart defects. IV drug abusers are at an increased risk. Endocarditis generally occurs when bacteria, fungi or other germs from another part of your body, such as your mouth, spread through your bloodstream and attach to damaged areas in your heart. If it's not treated quickly, endocarditis can damage or destroy your heart valves and can lead to life-threatening complications.
This condition needs expert doctors to diagnose and manage this condition. Antibiotic choices have to pinpoint and surgery should be considered if patient is worsening
Common signs and symptoms of endocarditis include
- fever and chills
- Fatigue
- Aching joints and muscles
- Night sweats
Myocarditis, a rare disease marked by inflammation and damage of the heart muscle caused by a viral infection or an autoimmune response.
Pericarditis, swelling and irritation of the pericardium, the thin sac-like membrane that surrounds your heart. This condition may be caused by infections or non infectious diseases as well. Commonest infective cause of pericarditis in India is tuberculosis.
Urinary Tract Infections
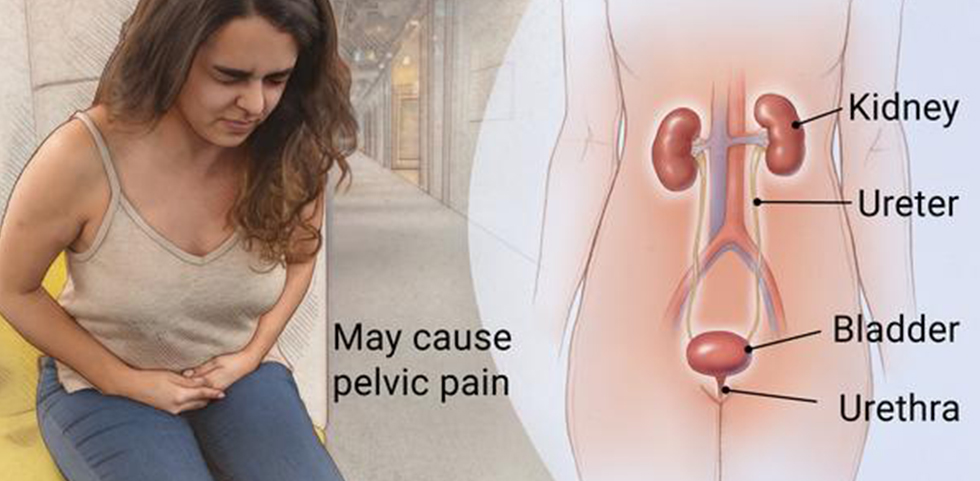
Urinary tract infections are more common in women. They usually occur in the bladder or urethra, but more serious infections involve the kidney. A bladder infection may cause pelvic pain, increased urge to urinate, pain with urination and blood in the urine. A kidney infection may cause back pain, nausea, vomiting and fever.
Symptoms :
- A strong, persistent urge to urinate
- A burning sensation when urinating
- Passing frequent, small amounts of urine
- Urine that appears cloudy
- Urine that appears red, bright pink or cola-colored — a sign of blood in the urine
- Recurrent Urinary tract infection especially needs attention from an infection specialist to avoid unnecessary higher antibiotics and avoid developing resistant infections.
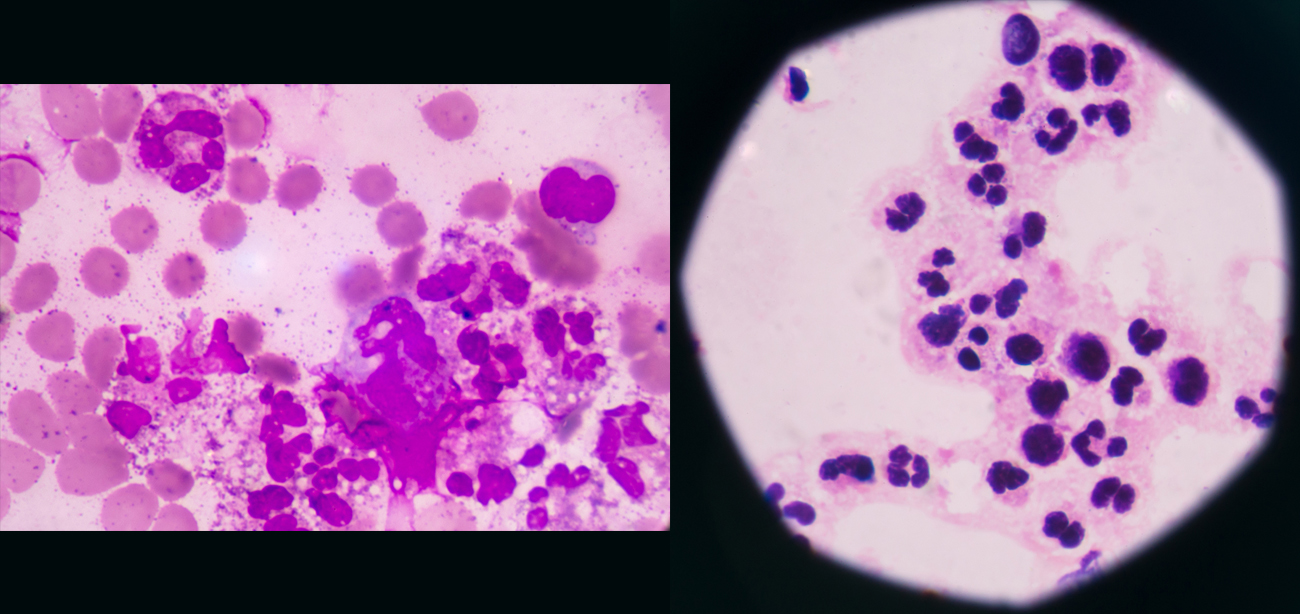
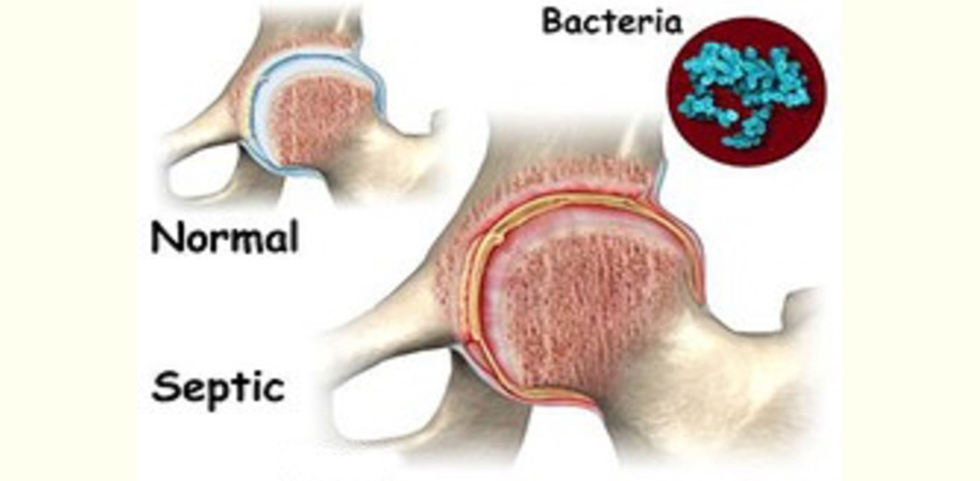
Bone and Joint Infections
These infections can broadly be considered as two types. One in native joint/bone, the other in implant cases. In former cases bacterial, tuberculosis and rarely fungal infections are more common. In the later a wide variety of infections may be seen.
In either cases, an approach which ascertains exact nature of infection is important. Treatment with antibiotics, antifungals, has to be appropriately chosen such that the medication reaches the bone tissue adequately. Also treatment in these infections is prolonged so sideffects of medicines has to be appropriately monitored.
An infection disease specialist is extensively trained in managing these cases.